The 9 Best Internal Audit Software in 2024
























Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
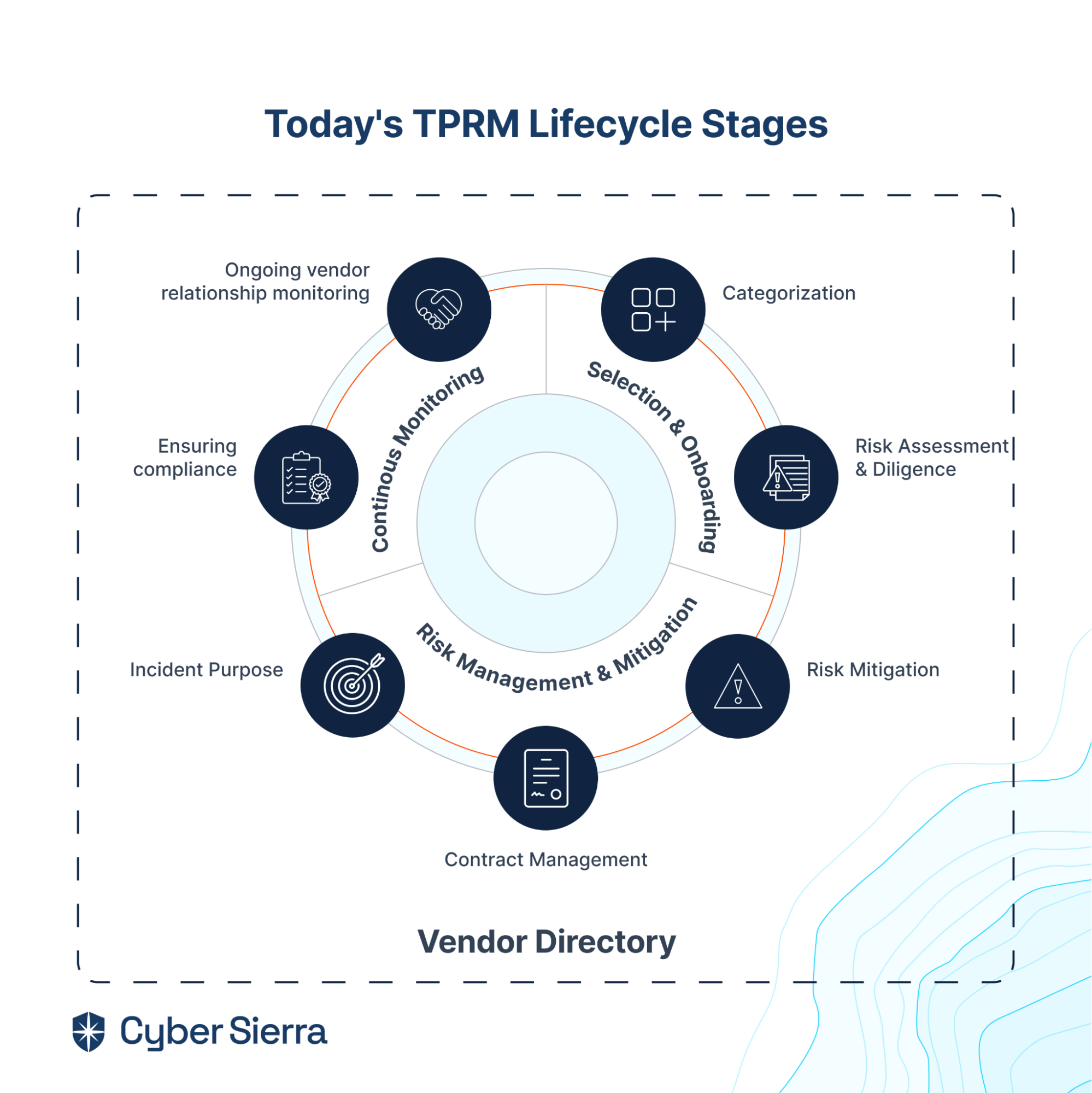
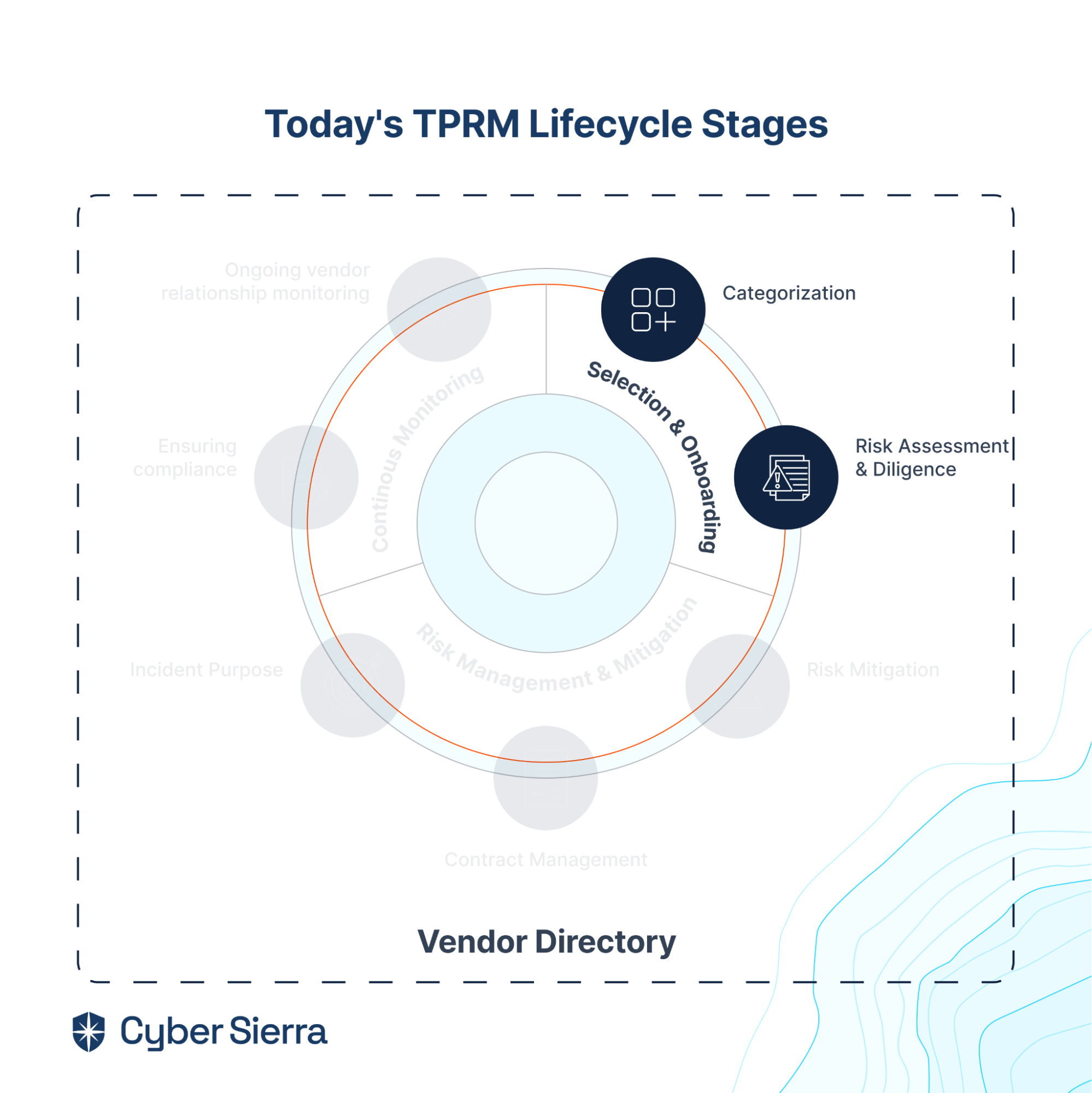
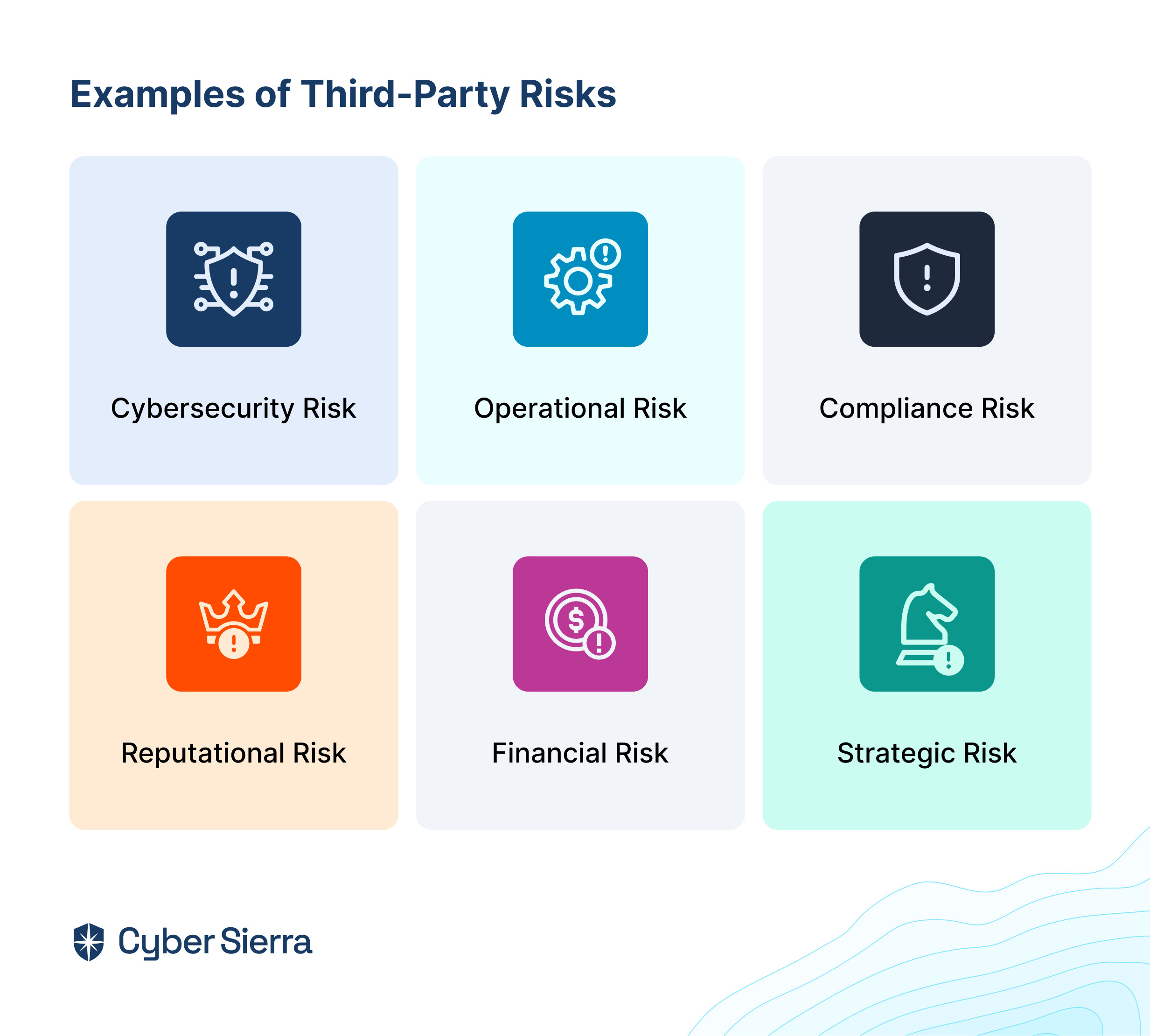
In today's fast-changing business environment, internal audit management software has become extremely crucial for organizations looking to simplify their audit processes while ensuring compliance and improving overall audit efficiency. While manual auditing is still a thing, software usage is preferred over manual internal audits because manual audits can prove to be cumbersome and less effective, and they are prone to look over potential weaknesses.
While there are several internal audit software solutions out there, choosing the right one can be overwhelming, as there are several variables to consider. To help you make an informed decision when choosing the best internal audit management software, we've compiled a detailed list of the nine best internal audit software in 2024.
What is Internal Audit Management Software?
Internal audit management software is a specialized tool designed to help various organizations strategize, execute, and supervise internal audits. These software solutions are indispensable for audit teams because they help simplify internal auditing processes, such as tracking audit progress and ensuring adherence to the organization’s regulations and internal policies. Internal audit software usually features solutions for an organization’s audit planning, risk assessment, document management, issue tracking, and reporting features.
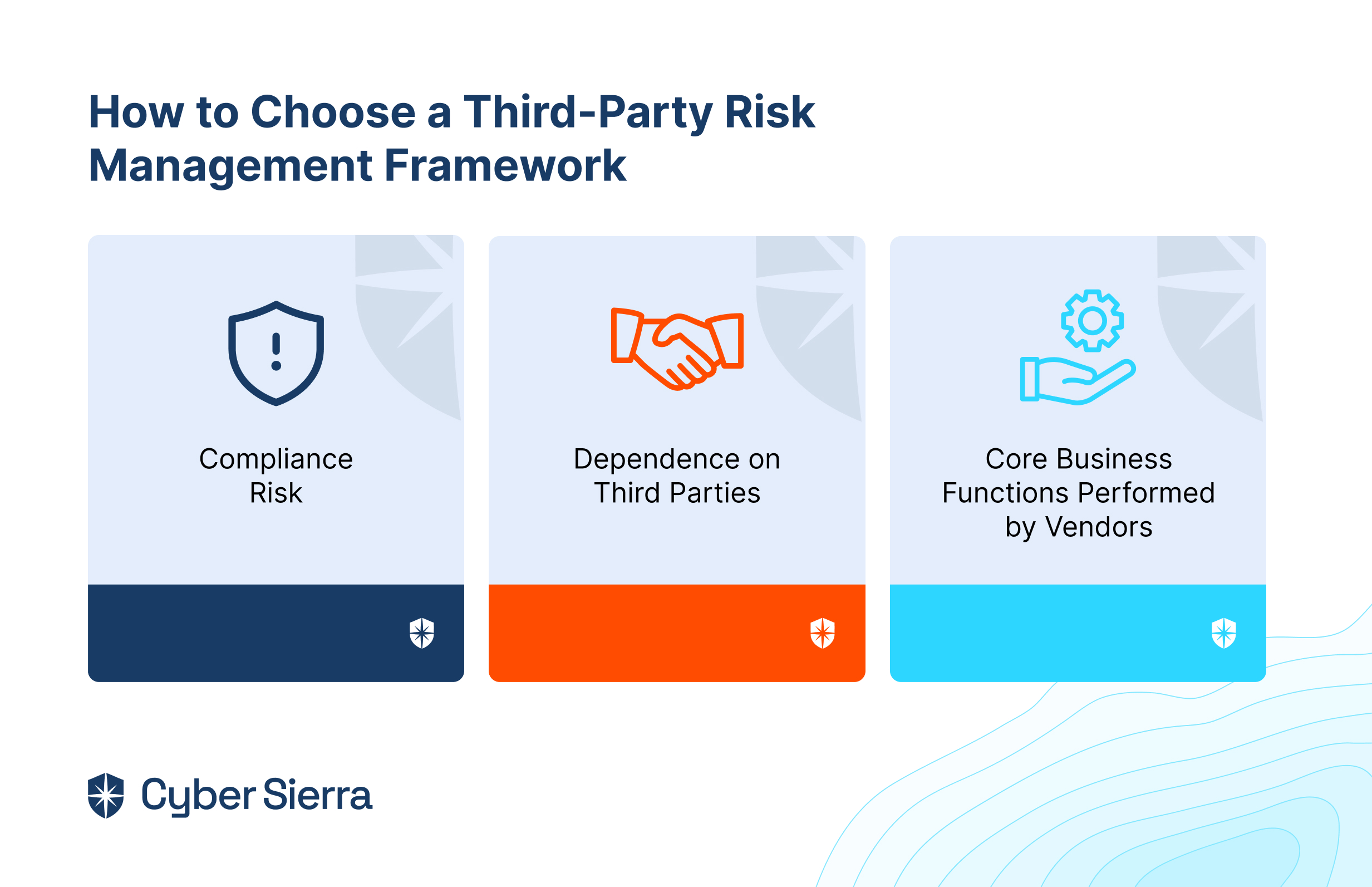
How to Choose the Best Internal Audit Software
When choosing internal audit software for your organization, you must consider a few factors to ensure you have chosen the best software that covers all your needs. Listed below are the factors that you must consider:
- Software Features: First and foremost, you must always look for software that offers a detailed set of features that meet your organization’s needs with regards to audit management requirements, such as planning audits, assessing risks, managing documents, and tracking and reporting issues.
- Integration of the Software: Always ensure that the software you choose effortlessly integrates with your organization’s existing systems, such as ERP or accounting software, to simplify data transfer and improve efficiency.
- Scalability: You must choose software that can aid your organization's growth by allowing you to add users and features as needed.
- User-Friendliness of the Software: If the software's task is to simplify your work, it should be easy to use and intuitive. Consequently, your audit team should be able to adopt it quickly without extensive training, thanks to its user-friendliness.
- Compliance with the Software: To ensure the security and integrity of your audit data, you must ensure that the software complies with relevant regulations and standards, such as SOX, GDPR, and ISO.
- Support: When choosing software vendors, look for vendors offering excellent training and customer support that will help you resolve any issues or questions that may arise during the implementation and use of the software.
- Pricing: Pricing plays a crucial role when choosing your internal audit software. While opting for a low-priced solution can be tempting, they often lack critical functionalities. Therefore, choose a solution that fits your organization’s budget while still containing all essential features. Also, ensure that the proposed pricing includes all necessary features and services because some software solutions offer add-on features at an additional cost.
The Best Internal Audit Software of 2024
Now that we know what internal audit management software is and how to choose one that works best for your organization, let’s dive right in and explore nine of the best internal audit software in 2024:
Cyber Sierra
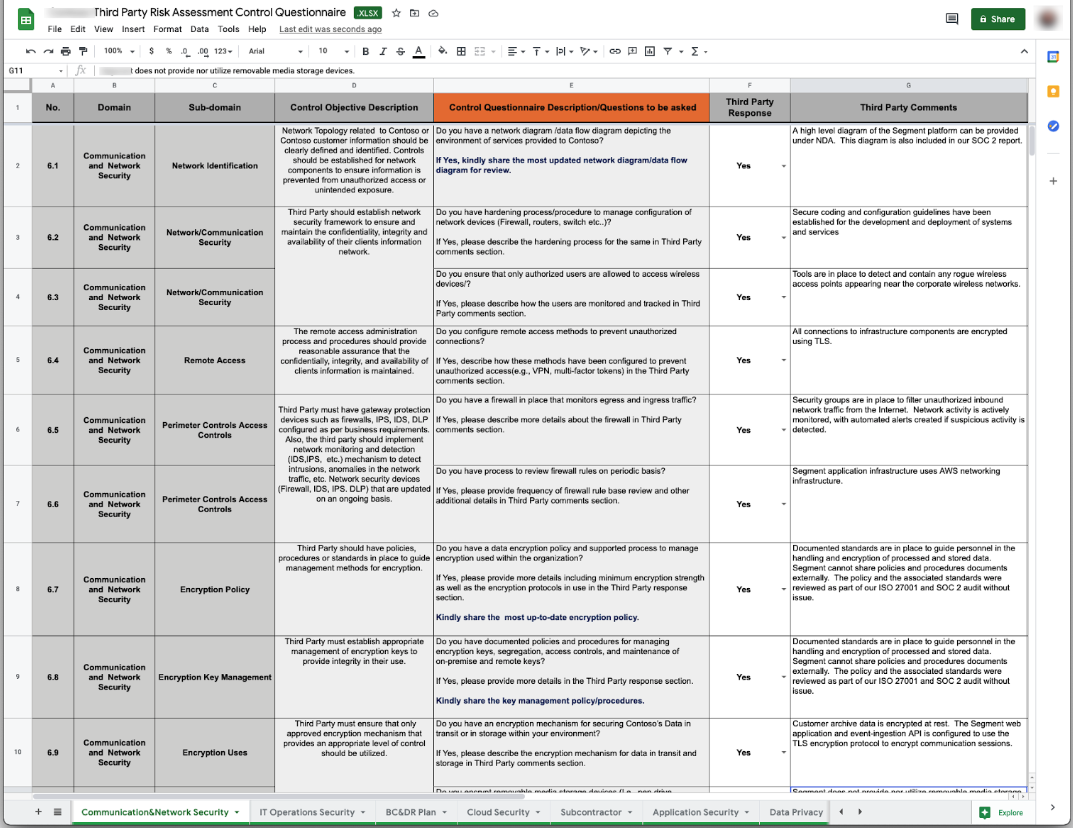
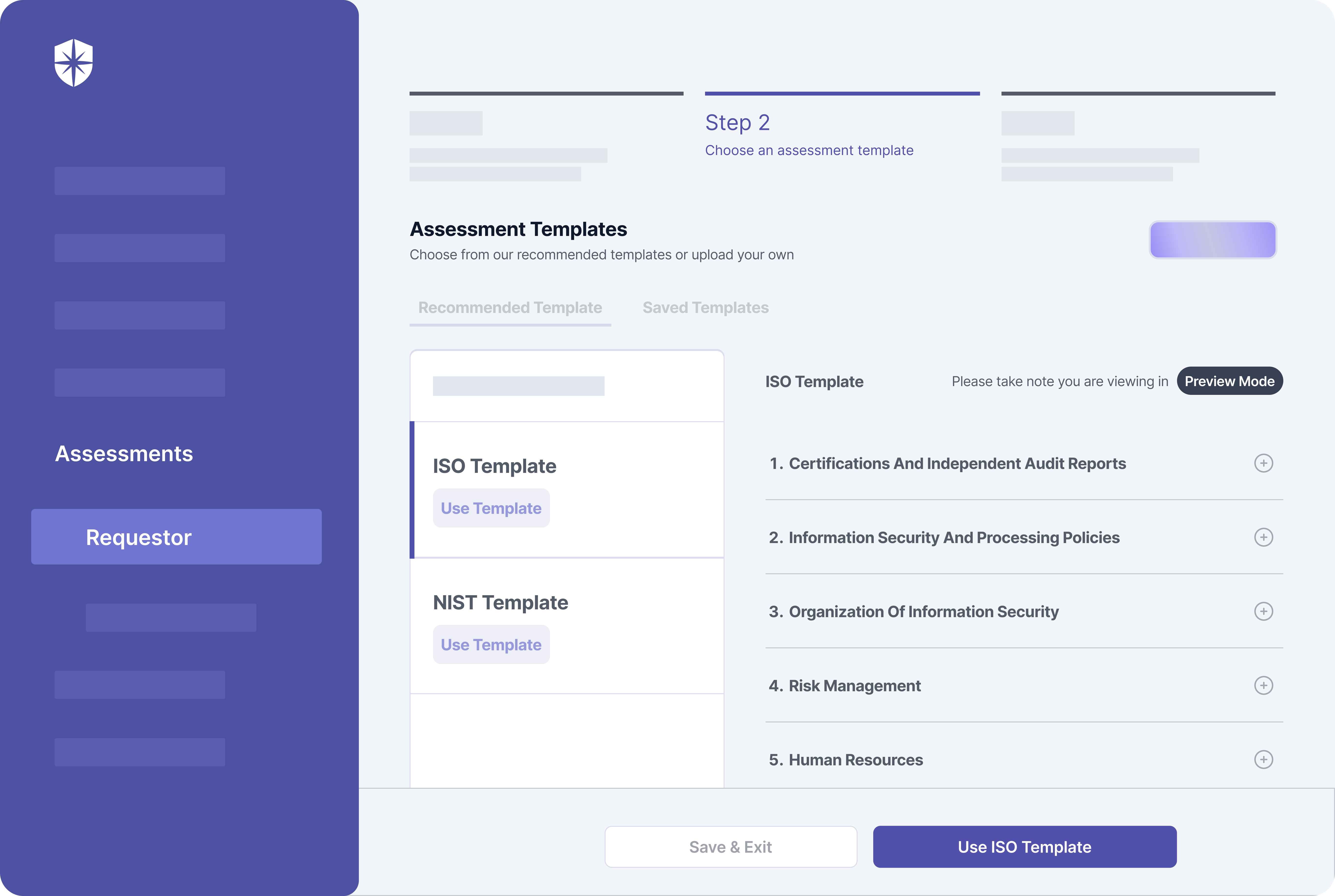
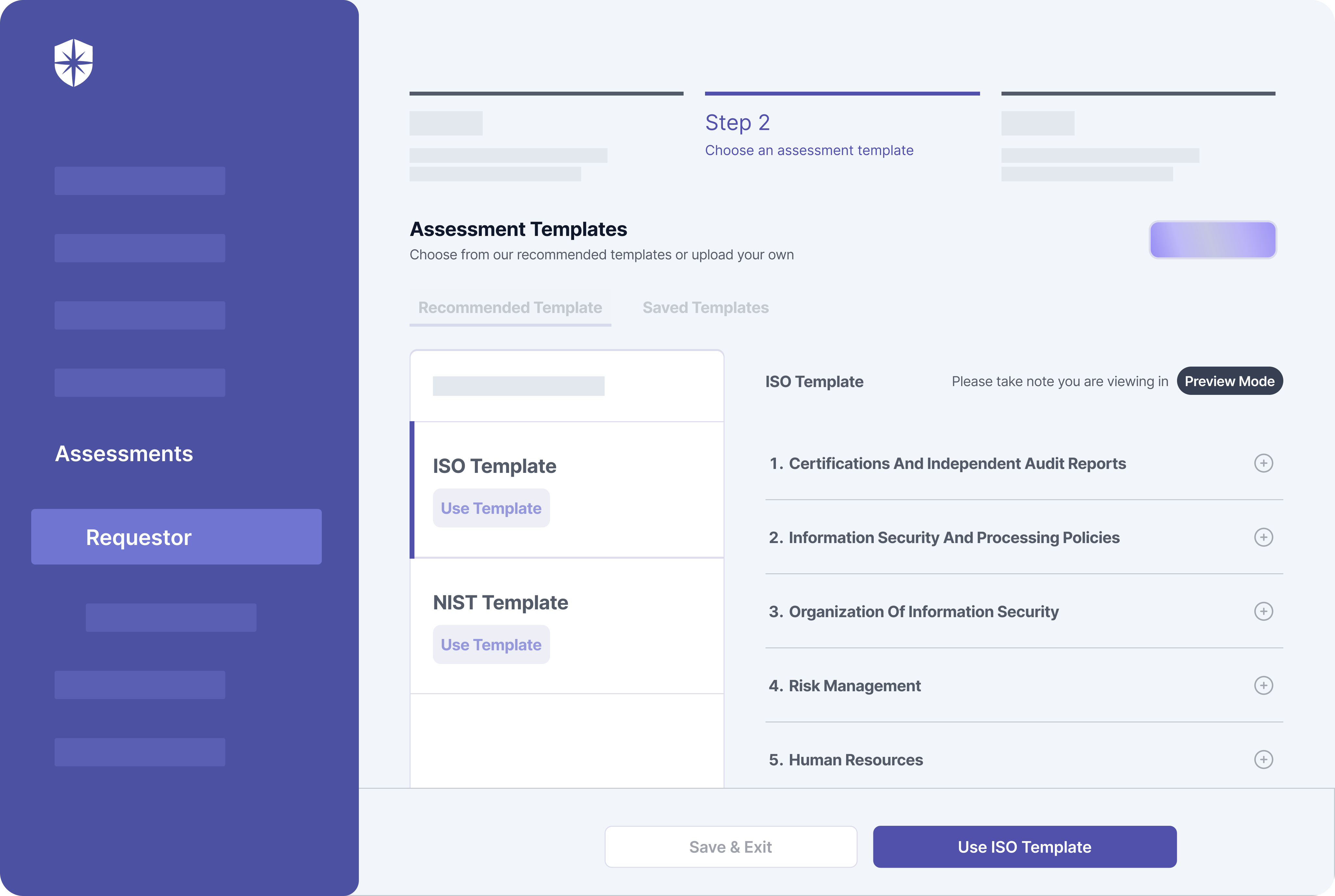
Cyber Sierra’s is an end-to-end GRC automation platform offers a comprehensive suite of tools tailored to streamline security compliance easy for enterprises. With continuous control monitoring and effective risk management modules the platform facilitates internal audits seamlessly. Providing a real-time intuitive dashboard with centralized controls repository, and audit ready programs, the software offers clear visibility into your security controls and conducts entity level checks to identify areas of non compliance during internal audits.
| Pros | Cons |
| Automated workflows for repetitive GRC tasks with prebuilt customizable templates. | The platform is built for enterprises, and hence may be slightly expensive for start-ups. |
| Extensive customization and scalability for improved productivity and efficiency. | |
| Seamless integration and easy to use interface. | |
| Automated evidence collection | |
| Along with GRC the platform also offer threat intelligence and TPRM programs |
Key Features of Cyber Sierra’s Internal Audit Software:
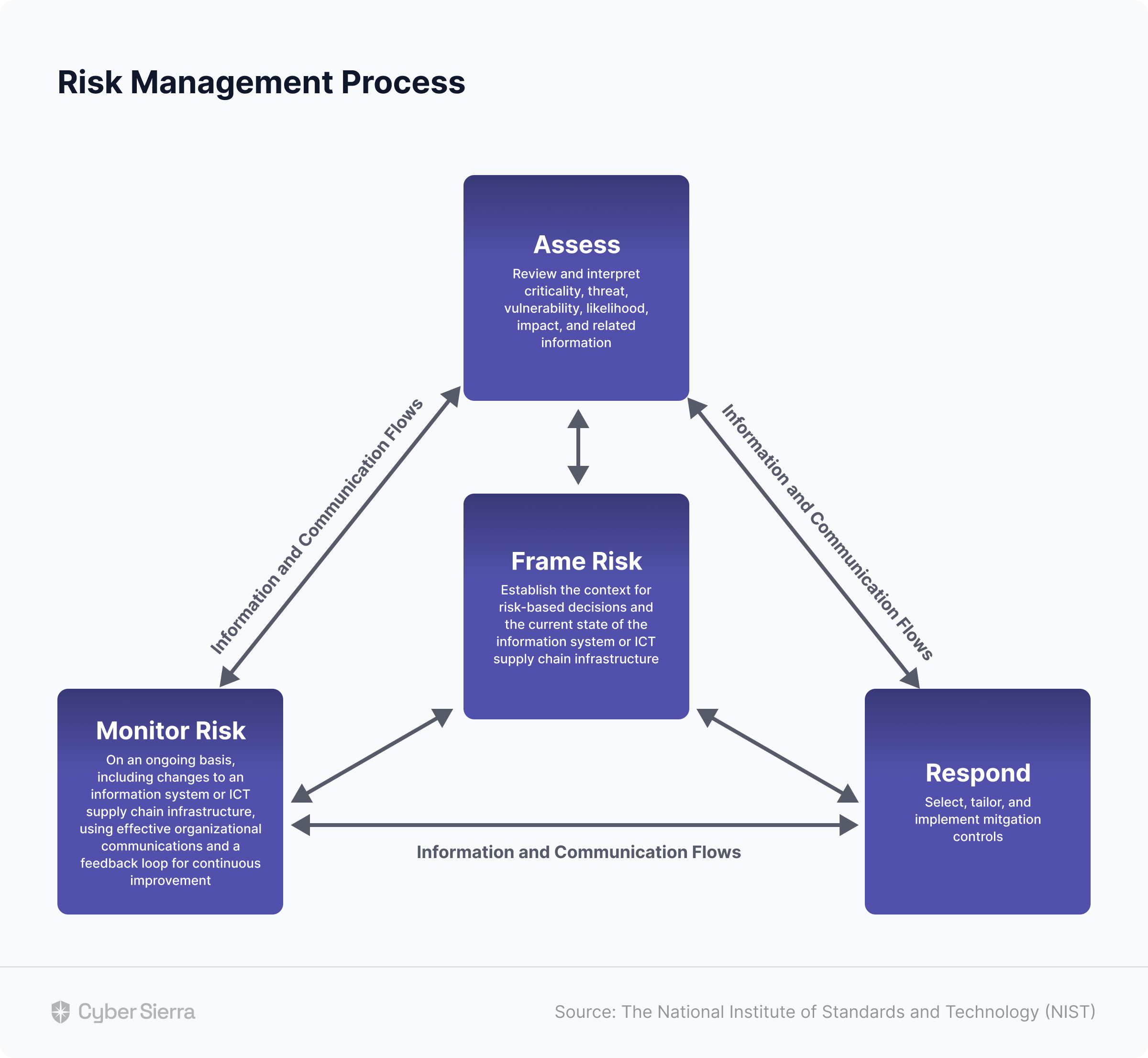
- Robust risk identification, evaluation and mitigation features to effectively manage poentential risk and threat across the enterprise.
- The software offers real-time monitoring caoablities with advanced reporting features providing data driven insights to support internal audits.
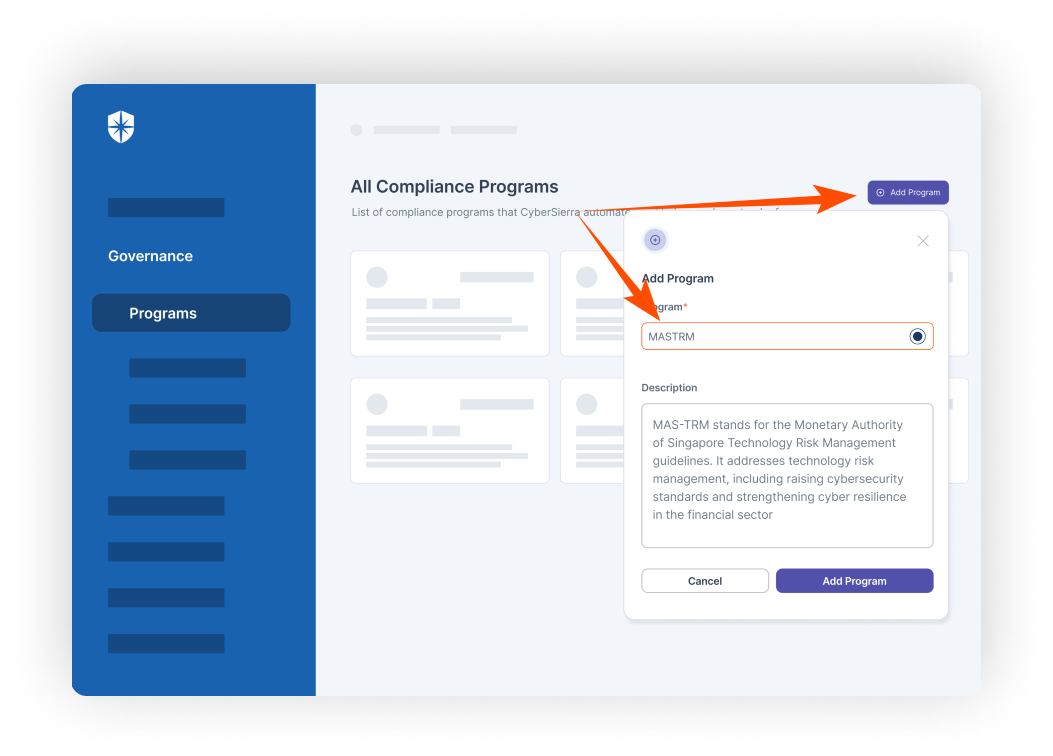
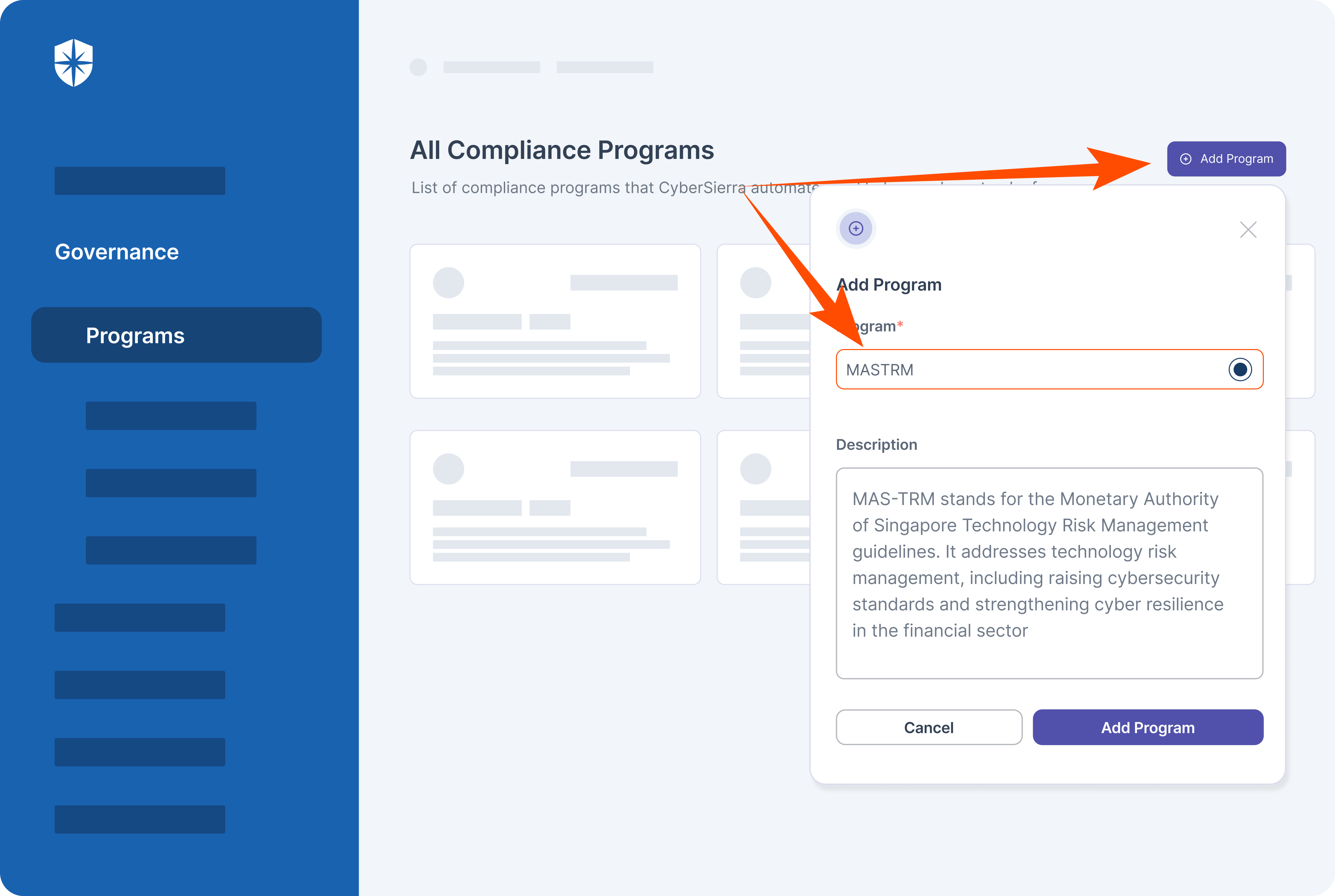
- Compliance automation modules for frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC and supports financial regulations including MAS-TRM, SEBI, CIRMP and more.
- The platform continuously updates it alogorims and adapts as per the evolving regulatory frameworks.
- Streamlines creating, monitoring and tracking of data management and policy repository including reviews and updates.
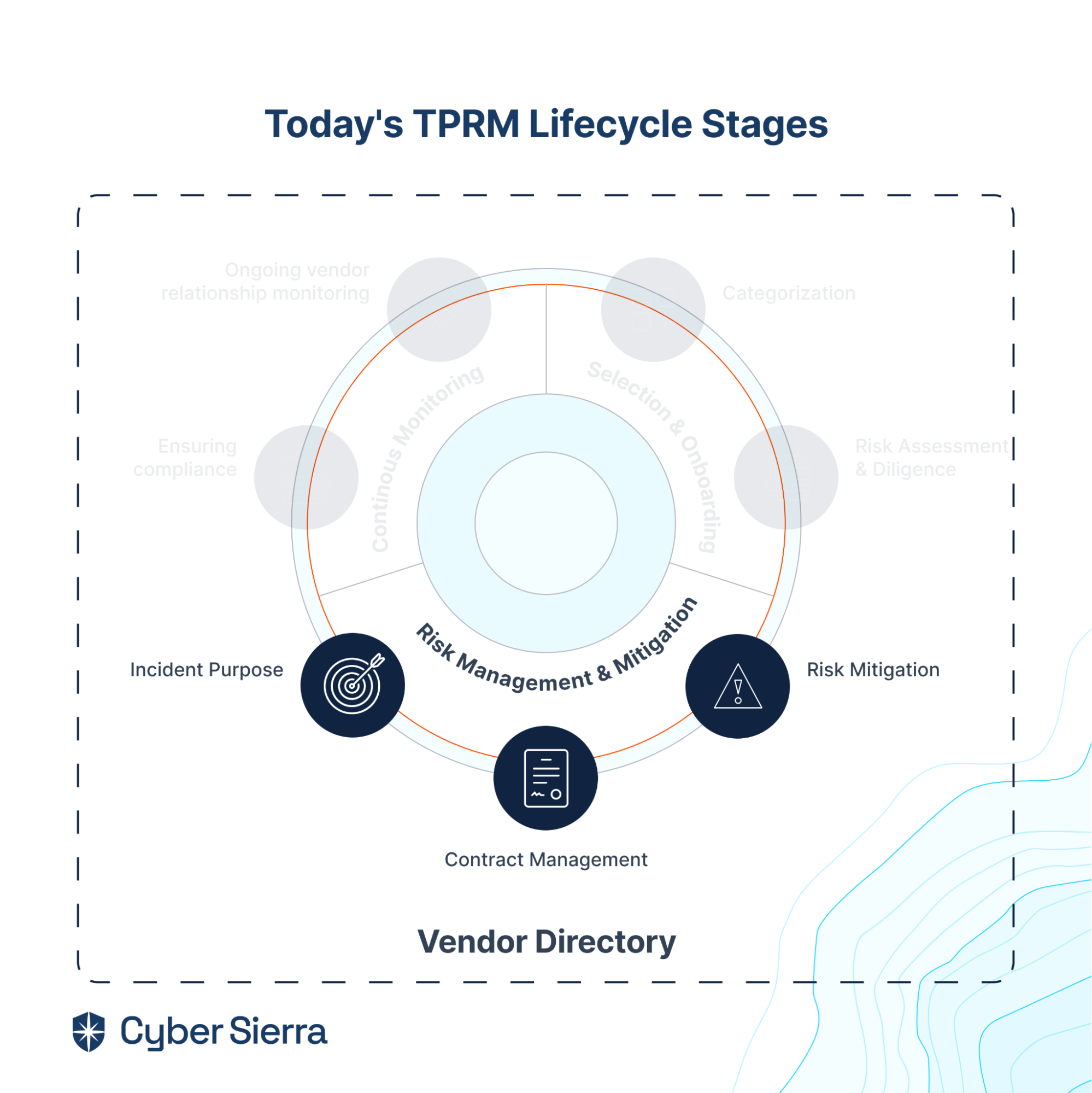
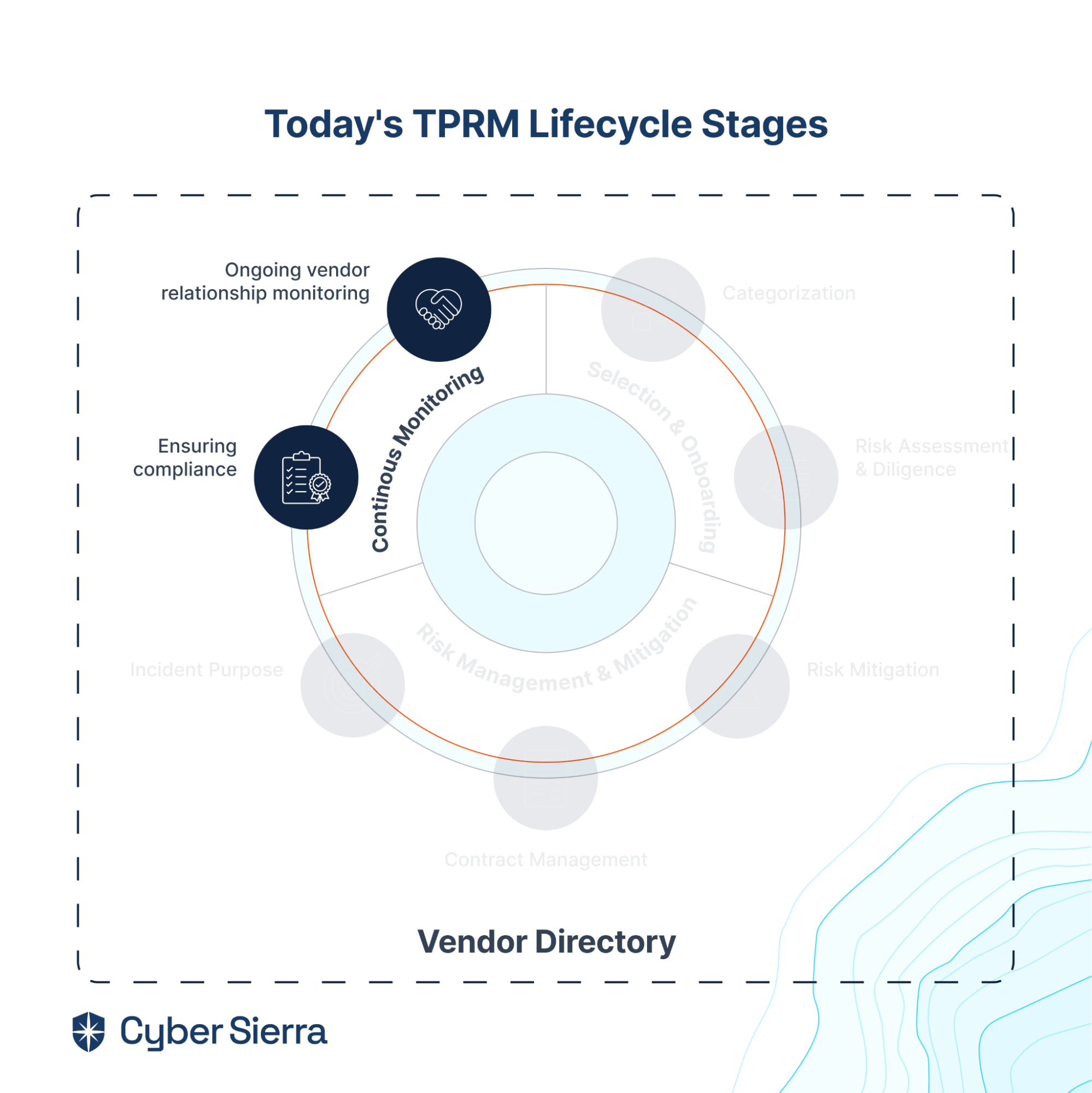
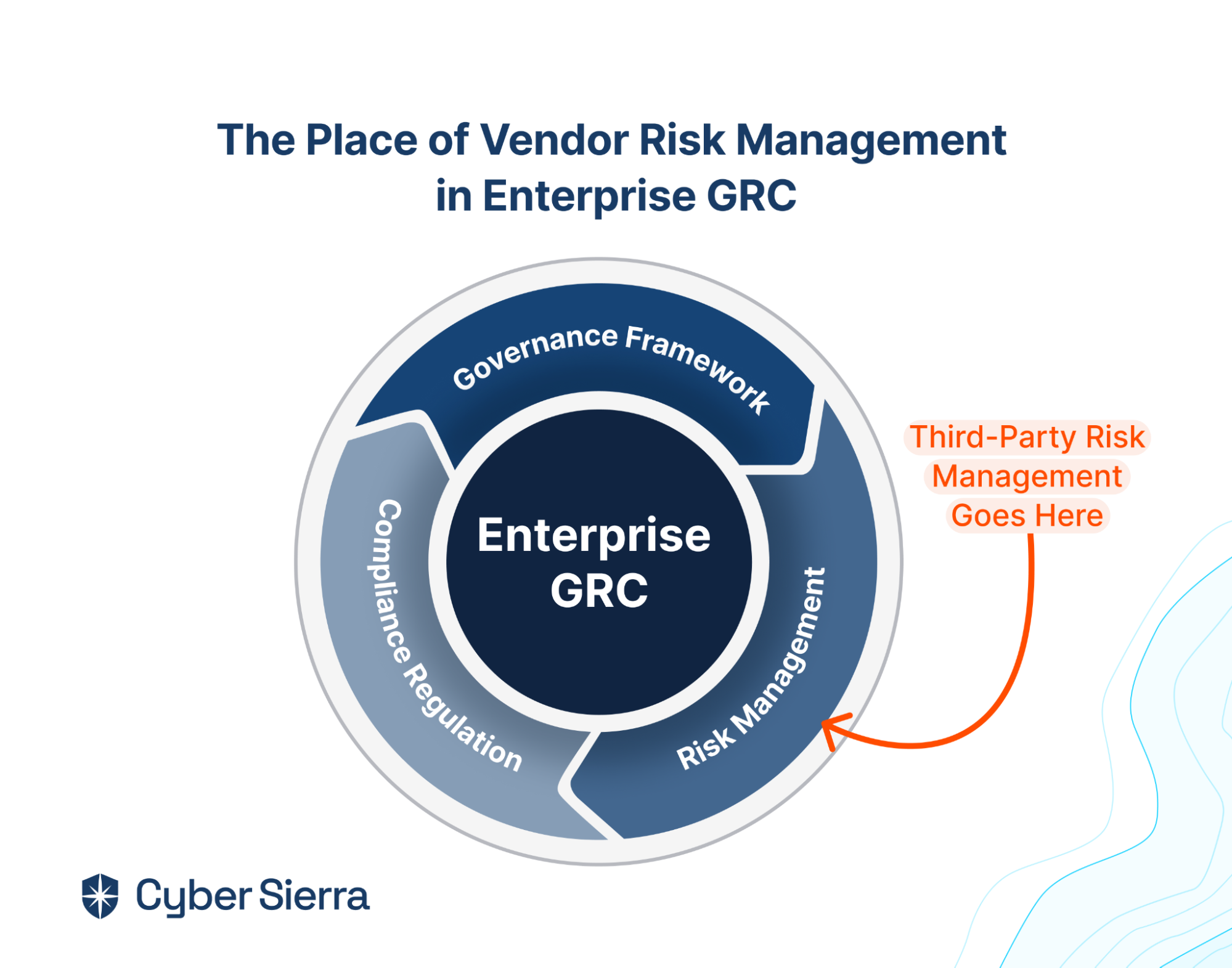
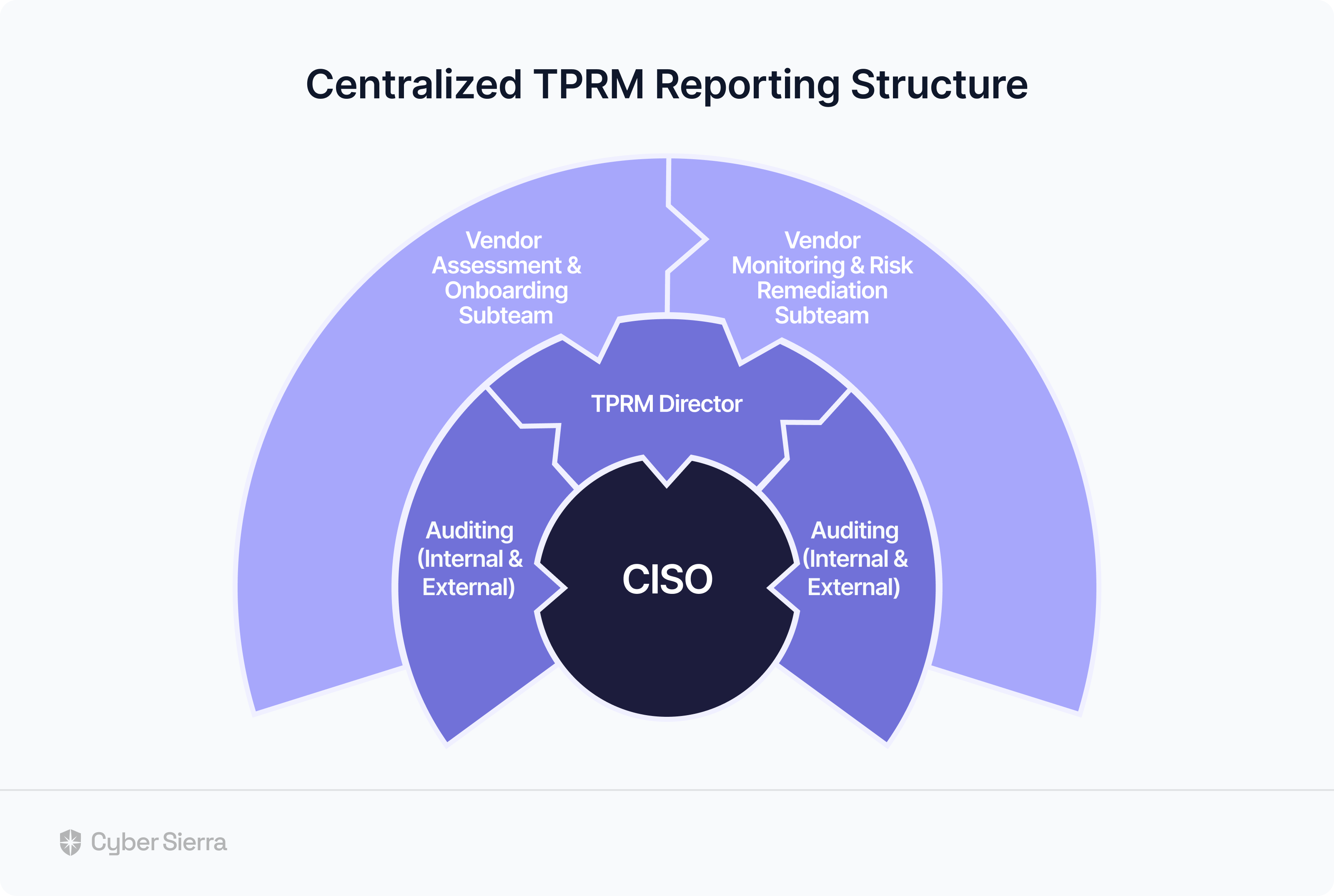
- It also offers smart GRC, third-party risk management, continuous control monitoring, threat intelligence, employee security training and cyber insurance - all from a single unified platform.
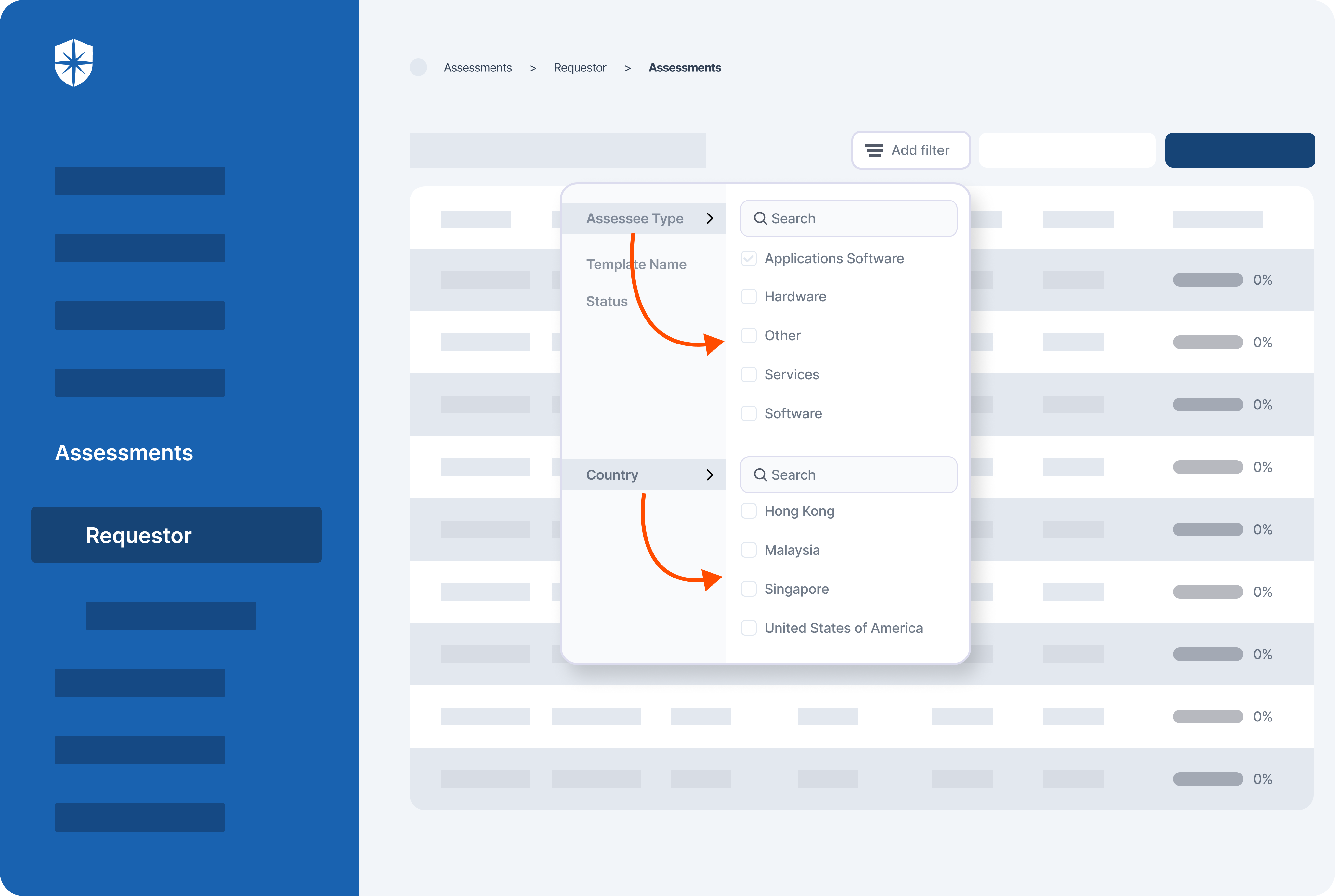
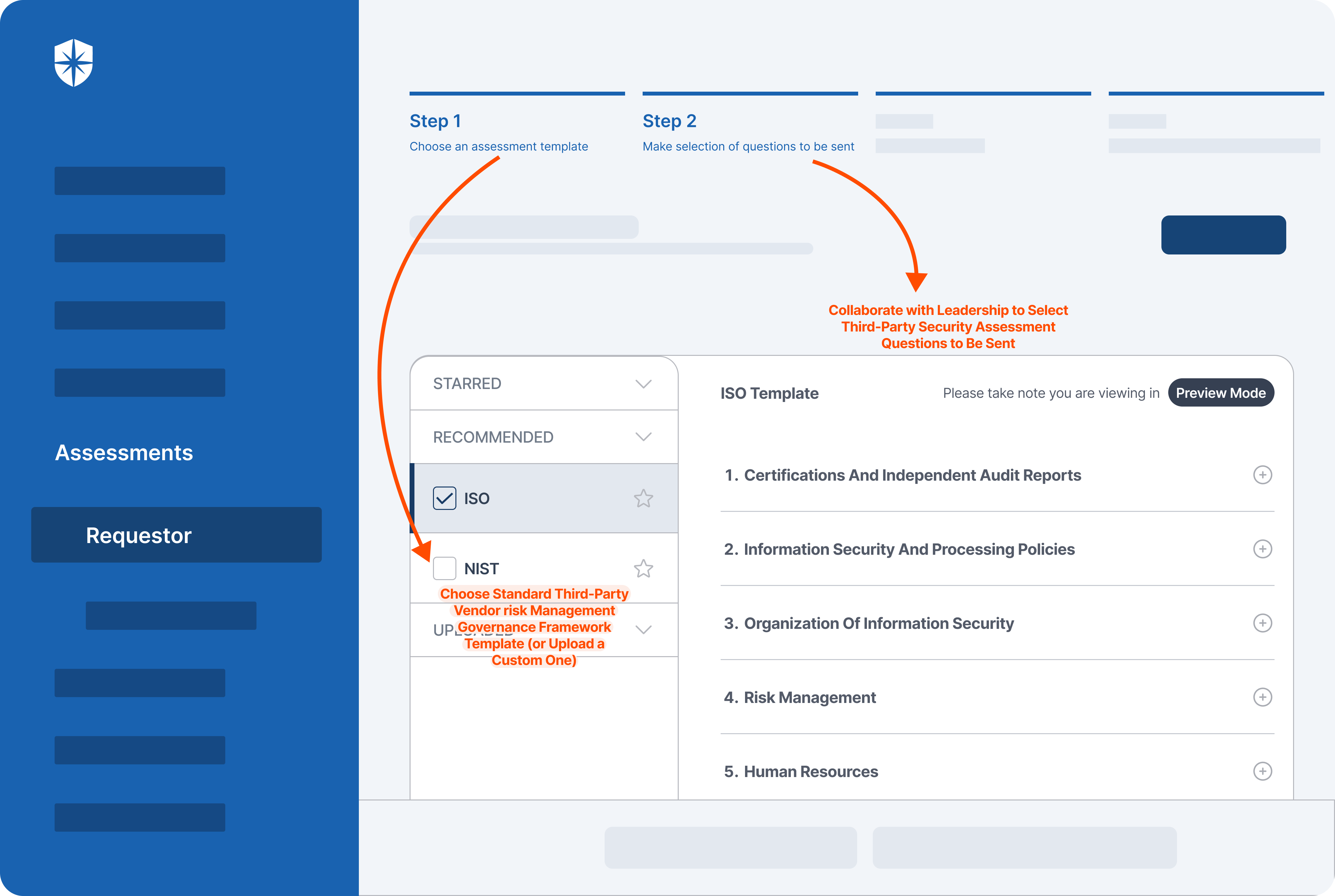
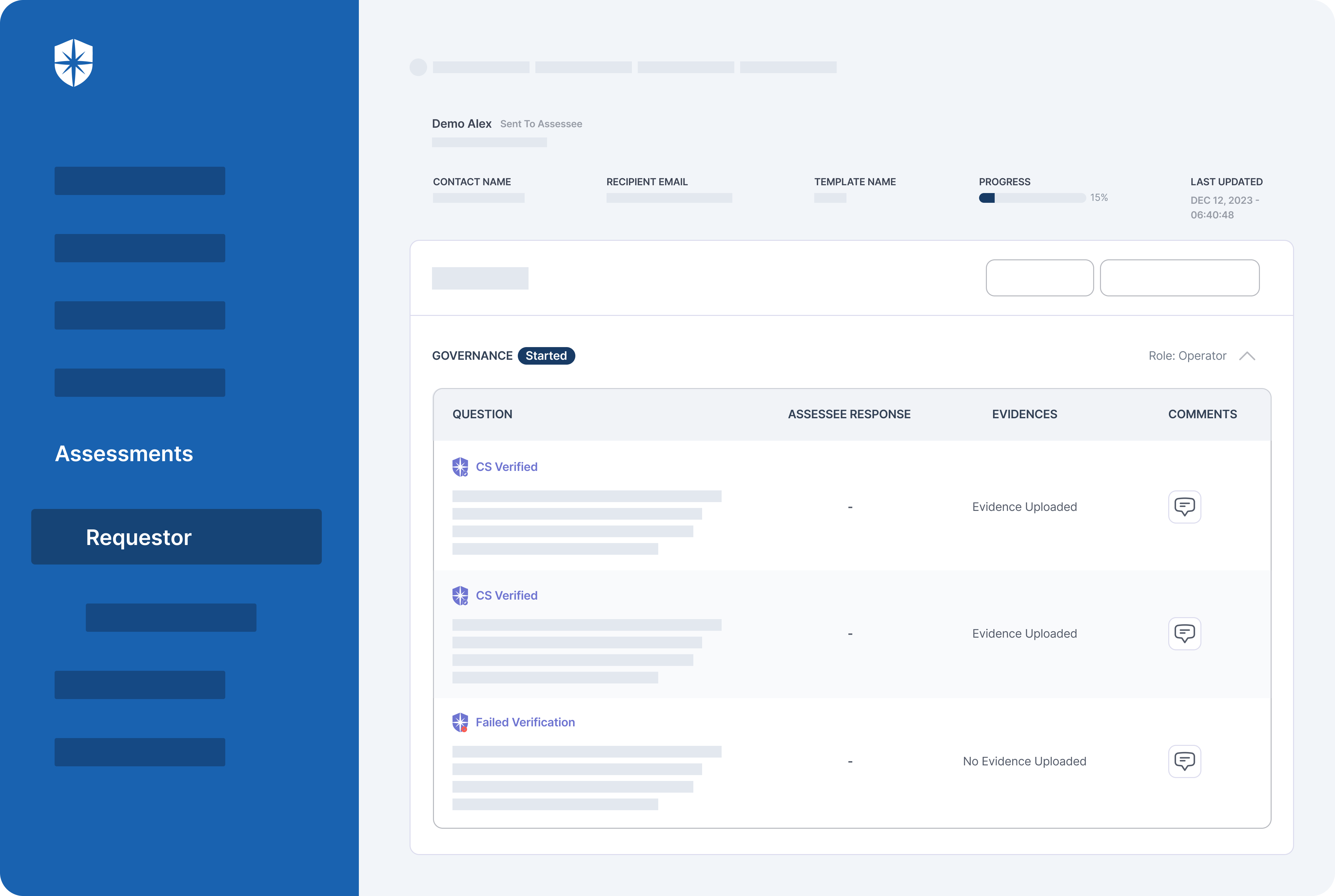
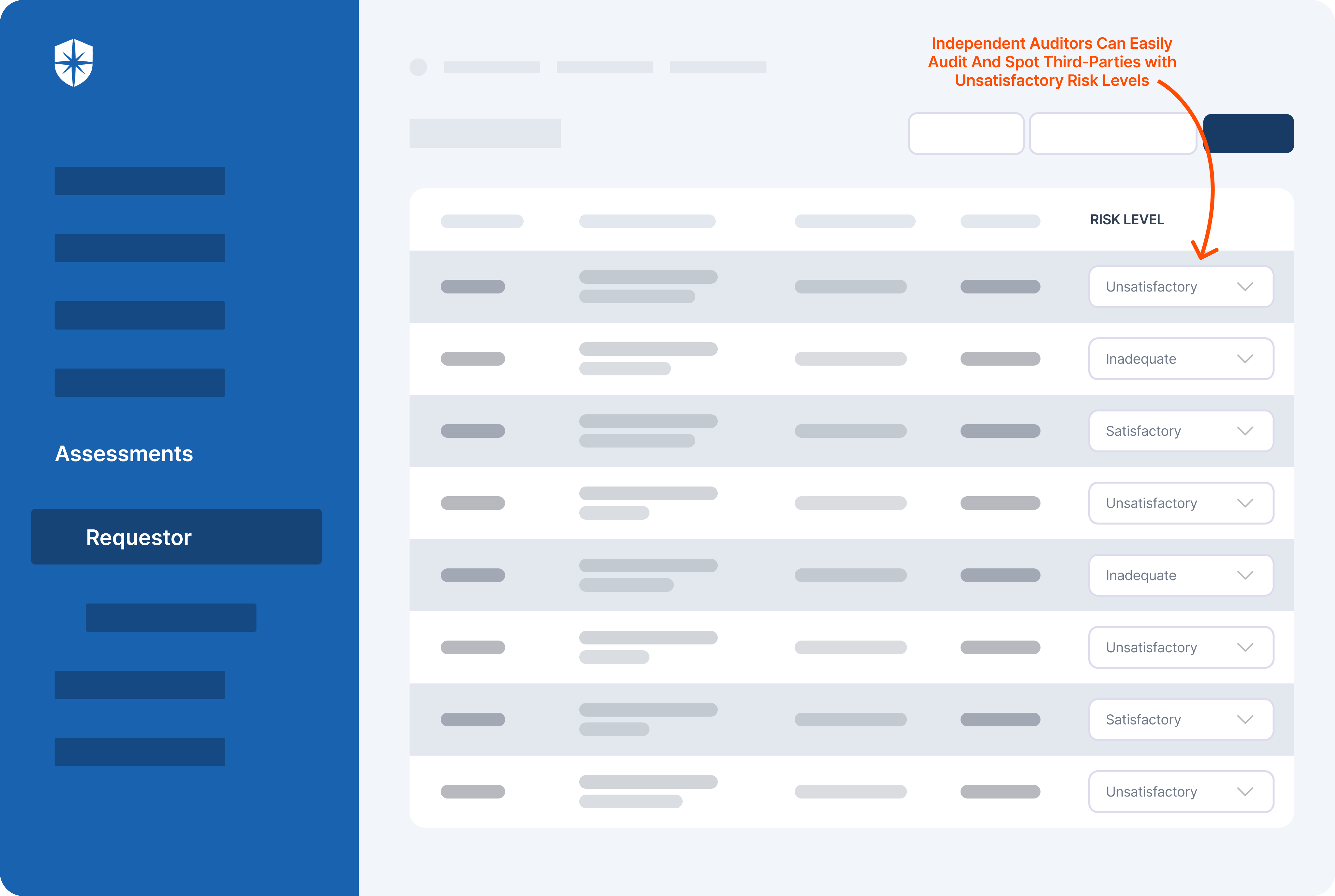
Cyber Sierra's AI-enabled platform has a Governance module to digitize compliance programs. It utilizes a multi-LLM approach to map vulnerabilities to controls, assets, and compliance programs. This facilitates continuous control monitoring and continuous third party risk management. Such capabilities are critical for enterprises that, on average, contend with over 500 technical controls daily, emphasizing the need for automation capabilities.
Auditboard is a compliance management platform that offers intelligent cloud-based audit management software with a wide range of features to help various enterprises manage their internal audits. It includes modules for collaborative audit planning, risk assessment, issue tracking, reporting, and closing security gaps.
| Pros | Cons |
| They offer a user-friendly interface | The customer support isn’t as responsive |
| The platform has strong reporting capabilities | They have limited customization options |
| The software can seamlessly integrate with other systems | Decreased cross-integration with other platforms/software |
| It is the best for maintaining an audit trail |
Key Features of Auditboard’s Internal Audit Software:
- Offers a simple cloud-based audit management system
- Audit planning and execution
- Excellent risk assessment and relief
- Good at issue tracking and resolution
- Easy to integrate with other systems
- Has an enhanced control program
Additionally, Auditboard is known for its strong reporting capabilities. That way, the software centralizes visibility and minimizes redundancies, allowing organizations to create simple customized reports that meet their needs. The software also offers a user-friendly interface, making it easy for audit teams to explore and use.
Workiva
Like Auditboard, Workiva is a cloud-based platform that offers a suite of audit, risk, and compliance management solutions. These include integrated governance, audit planning, risk assessment, document management, and reporting features.
| Pros | Cons |
| The software’s user interface is easy to use | Might face lag when switching between pages |
| It has a fairly flexible customization option | Average customer support |
| It has excellent collaboration features | It might lack advanced features that are usually offered by other software |
| The price might be high for new organizations |
Key Features of Workiva’s Internal Audit Software:
- Offers a simple cloud-based platform
- Internal audits via Workiva save time
- Allows the audit team to focus on the analytical activities
- Its reporting is customizable
- Effortlessly integrates with other systems
Additionally, Workiva is known for its assured integrated reporting and strong collaboration features, which allow audit teams to collaborate in real-time on various projects that are being audited. The software also offers flexible customization options, allowing organizations to tailor it to meet their needs.
SAP Audit Management
SAP Audit Management is a solution offered by the SAP suite of products. The SAP audit management software offers features aligning your organization’s business with audit planning, execution, and reporting. It integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules and offers strong analytical capabilities.
| Pros | Cons |
| This software can seamlessly integrate with the organization along with all the other solutions SAP offers. | It might be pricey for small, up-and-coming organizations |
| This software has advanced analytics capabilities | Beginners can find it hard to learn the various processes |
| It can optimize staff utilization and resource planning | |
| It has a strong reporting feature |
Key Features of SAP’s Internal Audit Software:
- Amazing and seamless integrated audit management within the SAP suite
- Risk assessment and management
What makes SAP Audit Management one of the best internal audit management software is that it can seamlessly integrate with other SAP modules, allowing organizations to streamline their audit processes. The software also offers advanced analytics capabilities, allowing organizations to gain insights from their audit data.
TeamMate+
TeamMate+ is an audit management software that aims to assist audit teams and effectively move through the audit workflow by offering features for planning audits, executing internal audits, and reporting discrepancies. It includes modules for risk assessment, issue tracking, and document management.
| Pros | Cons |
| End-to-end audit management and workflow solution. | The software has limited integration options with other systems |
| It has an intuitive user interface | Possibility of lacking a few advanced features that are offered by the other software. |
| Strong and comprehensive reporting capabilities | Document requests can only be sent one person at a time |
| The software is best when it comes to collaborative features |
Key Features of TeamMate+’s Internal Audit Software:
- It is one of the best document management software
- The internal audit’s planning and execution are always risk-focused.
- Has real-time collaboration
- The reporting is customizable
- Can easily integrate with other systems
TeamMate+ is a platform that gives you cloud-hosted options and is best known for its intuitive user interface, which makes it easy for audit teams to explore, navigate, and use the software. The software’s strong collaboration features allow audit teams to work seamlessly on audit projects.
Diligent
Diligent One Platform is an integrated risk management platform that offers audit, risk, and compliance management features for all digital organizations. The offers of Diligent include various modules for audit planning, risk assessment, issue tracking, and reporting.
| Pros | Cons |
| Diligent has a comprehensive suite of features that many organizations can use | The price can be a little high for organizations that are just starting. |
| It can integrate easily with the organization’s software | It takes quite some time to learn how to use the software |
| It has flexible customization options |
Key Features of Diligent’s Internal Audit Software:
- One of the best-integrated risk management platform
- Seamless integration with other systems
- Comes with three apps: a projects app, a results app, and a reports app that shows automation workflow
Diligent is known for its comprehensive suite of features that allow organizations to manage all aspects of their audit, risk, and compliance processes using a singular platform. The software’s strong integration capabilities allow organizations to integrate with other systems to simplify their processes.
Archer Audit Management
Archer Audit Management is a component of the Archer suite of products that aims to transform the efficiency of your internal audit function and offers features for audit planning, quality, and issue management. The various modules include risk assessment, issue tracking, and document management.
| Pros | Cons |
| You can seamlessly integrate the software with the organization’s system while also integrating with all the other Archer software | It can be a little expensive |
| Powerful reporting capabilities | Requires specialized training for optimal use |
| The software has strong customization options |
Key Features of Archer’s Internal Audit Software:
- The Archer Audit Management software is a component of the Archer suite of products
- The software is great at document management, audit planning, and scheduling.
- Seamless integration with other Archer modules
Archer Audit Management is best known for its seamless integration with other Archer modules. This allows organizations to manage all audit processes in one platform and assess audit entities risk-wise.
Hyperproof
Hyperproof is compliance and risk management software that offers audit, risk, and compliance management features. It includes modules for compliance operations, audit planning, risk assessment, issue tracking, and reporting.
| Pros | Cons |
| It has a user-friendly interface | It has limited customization options |
| Excellent collaborative features | It might lack some of the advanced features the other software produce |
| It has the capability to send reports comprehensively |
Key Features of Hyperproof’s Internal Audit Software:
- Allows you to collaborate with your auditors easily
- The software gives you seamless control over the controls and audit requests
- You can know the status of your audit
- Effortlessly integrates with other systems
Hyperproof is best known for its easy-to-use, user-friendly interface. This makes it one of the best internal audit management software for audit teams, as they can navigate and use it effortlessly. The software also offers excellent collaboration features, allowing audit teams to work together seamlessly on audit projects.
CURA
CURA is a governance, risk, and compliance software offering audit, risk, and compliance management features. The features offered by CURA include modules for audit planning, enterprise risk management, business risk management, risk assessment, issue tracking, and reporting.
| Pros | Cons |
| It has flexible customization options | The price of the software can be a little high |
| Its integration capabilities are exemplary | It takes time to master the software |
| It has a thorough reporting feature |
Key Features of CURA’s Internal Audit Software:
- CURA is one of the best governance, risk, and compliance management software
- The software’s strength lies in its issue-tracking and resolution capabilities
- It is flexible and user-friendly.
CURA is best known for its flexible customization options and user-friendliness. The platform allows organizations to tailor the software to their liking and needs. The software is also very particular about risk management and has modules that range from enterprise risk management and operational risk management to incident management and policy management.
Ready to Successfully Navigate Audits?
With organizations worldwide grappling with increasing regulatory pressures and escalating cybersecurity threats, the demand for an advanced solution that can effectively help you navigate these challenges has skyrocketed. An internal audit solution is the first step to adding to cyber resilience. Therefore, choosing the right solution is paramount to ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of your organization's internal audit processes.
The nine software solutions highlighted in this article offer a comprehensive range of features tailored to meet diverse organizational needs. Whether you require robust audit planning capabilities, seamless integration options, or comprehensive reporting features, there is a solution that can address your specific requirements and streamline your audit operations.
Here's how Cyber Sierra can facilitate your audit process
Cyber Sierra’s GRC program offers a robust suite of features such as advanced risk analytics, customizable compliance frameworks, and with the integration with technologies like AI the platform easily integrates with your existing tech infrastructure and maps to your GRC controls, and provides complete visibility into your security and compliance posture. To summarize, it puts your GRC program on autopilot and empowers your audit team to effortlessly manage and optimize audits, ensuring compliance while mitigating risks.
Schedule a demo today and discover how Cyber Sierra can transform your organization's audit landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between internal and external audit software?
Internal audit software: This software is designed for organizations to conduct internal audits. Internal audits usually focus on the organization’s internal operations, processes, and compliance.
External audit software: This software, on the other hand, is used by external audit firms to conduct audits on their clients. External audits usually focus on financial statements and regulatory compliance.
Can internal audit software integrate with other systems used by the organization?
Yes, internal audit software integrates with other systems used by most organizations. Often, internal audit software solutions offer integration capabilities with systems like ERP, accounting, and document management systems. This integration allows for simple yet seamless data transfer, collaboration, and improved efficiency in the audit process.
Is internal audit software suitable for small organizations?
Yes, internal audit software solutions are suitable for small organizations. In fact, they are also specifically designed for small organizations. More often than not, these solutions offer features with price plans that accommodate the needs and budgets of small organizations. .





















A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.